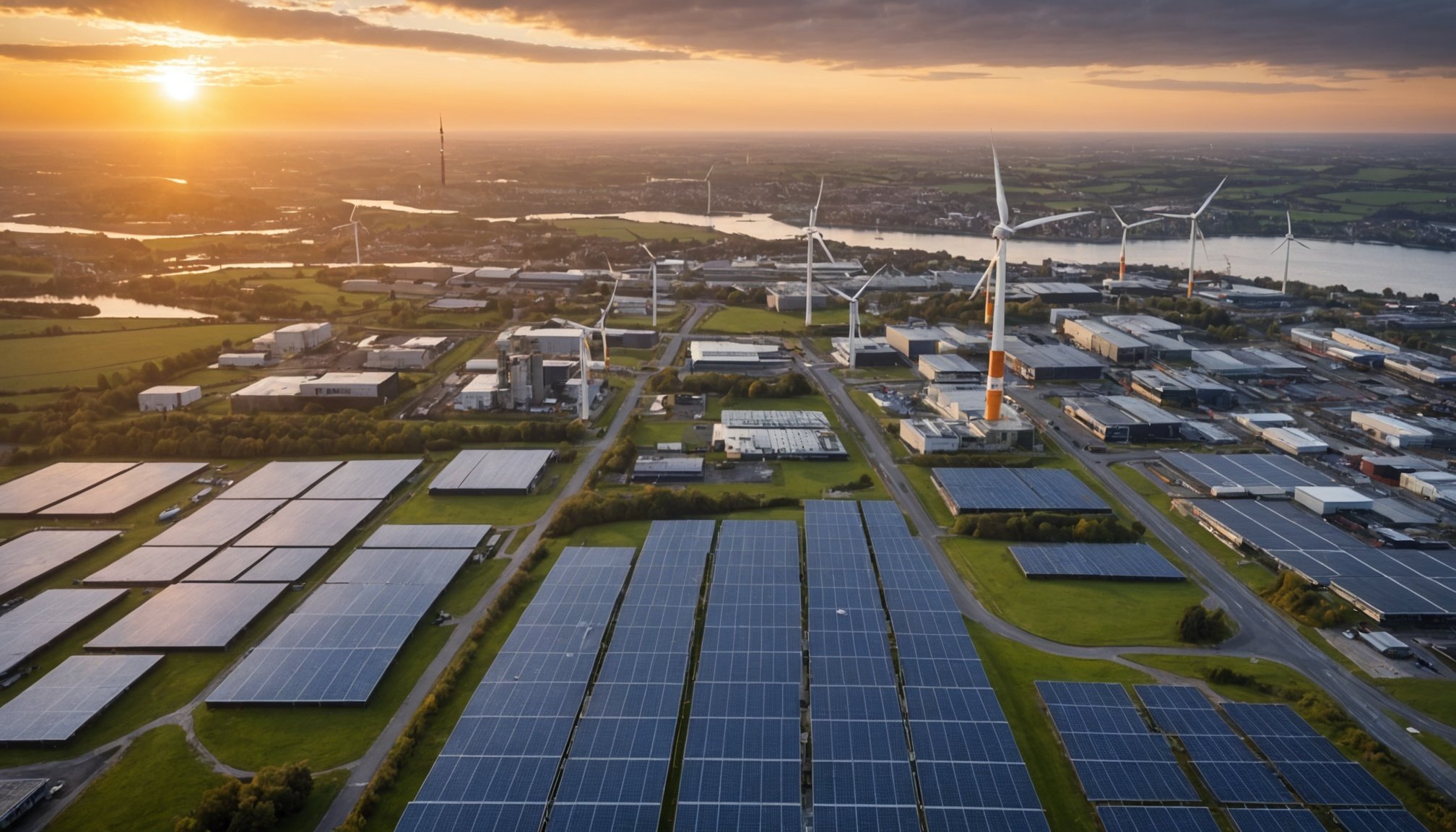
Overview of Smart Grid Technologies
At the forefront of modern energy systems, smart grid technologies integrate digital communication and information technology with the traditional electrical grid. These technologies aim to revolutionise the UK energy sector by improving energy management and efficiency. Smart grids comprise core components such as smart meters, sensors, and communication networks, which enable real-time monitoring and control of energy flow.
Historically, the development of smart grids in the UK has been driven by the need to enhance efficiency and adapt to increasing renewable energy sources. Over the past few decades, significant technological advancements have led to more sophisticated and responsive energy systems. This evolution highlights the growing importance of smart grids for effective energy management and sustainability efforts, ensuring they meet the demands of modern society.
In the same genre : Revolutionizing Urban Transit: Harnessing Big Data to Overhaul Public Transport in UK Cities
Furthermore, smart grids play a crucial role in facilitating the integration of various renewable energy sources such as wind and solar. They do this by dynamically adjusting to fluctuations in supply and demand, thereby maintaining grid stability. As the UK strives towards a low-carbon future, smart grid technologies are increasingly pivotal in achieving sustainable energy solutions.
Key Benefits of Smart Grids
Smart grids offer numerous benefits that are pivotal for modernising energy systems. One of the main advantages is enhanced energy efficiency. Smart grids minimise energy losses by intelligently managing electricity flow, leading to optimal use of resources. This efficiency also translates into cost savings and reduced environmental impact, making it a win-win for consumers and providers alike.
Also read : Futuristic threads: exploring the impact of e-textiles on fashion and technology in the uk
A significant aspect of smart grids is their ability to facilitate renewable integration. By accommodating fluctuating energy supplies from sources like wind and solar, smart grids ensure a steady and reliable energy supply. This adaptability is crucial as the UK increases its reliance on renewables to reduce CO2 emissions and move towards a sustainable energy future.
Additionally, improvements in reliability and resilience define the benefits of smart grids. With real-time monitoring capabilities, smart grids can quickly adapt to disruptions or energy demand changes. This responsiveness not only bolsters grid stability but also enhances security and reliability for consumers. Consequently, smart grid technologies pave the way for a more robust and responsive energy infrastructure, vital for the UK’s low-carbon ambitions.
Implementation of Smart Grid Technologies
The implementation of smart grid technologies involves several critical stages, each with unique challenges. Initially, extensive planning and evaluation are essential to align the smart grid infrastructure with the UK’s existing energy systems. This step is crucial to ensure a seamless integration that maximises the grid’s efficiency and potential.
Deployment challenges often stem from the financial and technical aspects of upgrading traditional grids. These challenges can include the high costs of new infrastructure and the complexity of technology integration. Overcoming these barriers requires strategic investment and collaboration across stakeholders in the UK energy sector.
Despite these obstacles, various strategies can encourage technology adoption. Engaging stakeholders through incentives and education can facilitate better understanding and commitment. This involvement is significant in promoting the benefits and long-term advantages of adopting smart grid technologies.
Moreover, the role of policy and regulatory bodies is pivotal in supporting and expediting the transition to smart grids. Regulatory frameworks should provide clear guidelines and support to assist stakeholders in overcoming these barriers. By addressing these core challenges, the UK can pave the way for a widespread and effective adoption of smart grid technologies.
Case Studies of Smart Grid Implementation in the UK
Examining smart grid case studies in the UK offers valuable insights into successful real-world applications. A noteworthy project is the Low Carbon London initiative, which significantly enhanced energy efficiency and grid management. This project used smart meters and advanced data analytics to balance energy demand, reducing costs and carbon emissions.
Another example is the Northern Isles New Energy Solutions (NINES) project. It showcased how smart grid technologies could facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind, by storing excess energy. NINES effectively demonstrated how renewable integration could maintain grid stability amidst fluctuating supplies.
Lessons from these UK projects suggest several key performance indicators essential for evaluating smart grids: energy efficiency, cost savings, renewable integration capability, and grid reliability. These indicators are crucial for measuring the success and scalability of smart grid technologies. As more projects emerge, understanding these benchmarks will help guide future development and maximise benefits across the UK energy sector, aligning with energy management goals.
Policy Implications and Regulatory Framework
Smart grid technologies demand a robust energy policy framework in the UK to facilitate seamless integration and adaptation. Current UK regulations focus on encouraging investment in smart infrastructure and ensuring compatibility with existing energy systems. The government plays a crucial role by creating incentives for the energy sector to embrace innovation while maintaining consumer protection and fair access to resources.
To promote smart grid technologies, regulatory bodies work towards establishing standard guidelines that ensure reliability, safety, and security. These measures not only support the technological transition but also aim to enhance consumer awareness and engagement with energy management systems. As smart grids evolve, regulation must keep pace with technological innovations, thus requiring a dynamic and flexible approach.
Future policy directions are expected to concentrate on fostering collaboration between stakeholders, ensuring data privacy, and promoting research and development in the realm of smart grids. By doing so, the UK can enhance its leadership in sustainable energy solutions, ensuring that smart grid governance aligns with the broader goals of reducing carbon emissions and increasing renewable energy integration. This future-ready approach aims to optimise the benefits of smart grids for the entire energy ecosystem.
Future Trends in Smart Grid Technologies
The future of smart grids is poised to be shaped by emerging technologies and evolving industry paradigms. Innovations in energy storage and data analytics are set to transform how energy is managed and consumed. By integrating advanced sensors and intelligent software, smart grids will become increasingly adept at predicting energy demand and optimising supply.
As the UK energy sector continues to embrace new technologies, there will be a greater emphasis on decentralised energy systems. This shift promotes resilience and flexibility, allowing communities to manage their own energy needs efficiently. Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence will enhance energy management, providing smarter solutions for balancing loads and facilitating renewable integration.
In terms of technological trends, the Internet of Things (IoT) will play a significant role. By connecting diverse devices within the energy ecosystem, IoT will enable seamless communication between systems, enhancing overall grid performance. Additionally, the rise of blockchain technology may introduce new models for energy exchange, fostering transparency and security in transactions.
These advancements hold the potential to revolutionise the smart grid landscape, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient energy future. As the next decade unfolds, these innovations will drive the UK towards a more resilient and responsive energy infrastructure.